Brygida Berse, Ph.D
 |
Adjunct Research Assistant Professor Contact Information
|
Education/Training –
- M.Sc., Molecular Biology, Warsaw University , Warsaw , Poland
- Ph.D., Biological Science, Warsaw University , Warsaw , Poland
- Visiting Scholar, Centre de Genetique Moleculaire du CNRS, Gif-sur-Yvette , France
- Postdoctoral Associate, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Cambridge , MA , USA
Appointments
1988-1994 Research Associate, Department of Pathology, Beth Israel Hospital, Boston, MA
1988-1995 Instructor, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
1994-1995 Research Associate, Department of Pathology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA
1996- present Research Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, MA
Research Interests –
My research focuses on the signal transduction pathways regulating gene expression in neuronal cells. The main line of studies relates to the two genes coding for acetyltransferase (ChAT) and vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT). They exhibit unusual genomic organization, i.e. the latter is entirely contained within the first intron of the former. This provides a very unique model to study coordinated regulation of genes involved in related functions, but it also presents specific challenges for promoter cloning and analysis. Cellular responses to extracellular factors, i.e. protein phosphorylation, nuclear translocation of transcription factors, promoter activity and specific mRNA accumulation are studied in neuronal cell lines and in primary neuronal cultures. Methods include tissue culture, mammalian cell transfection, recombinant DNA techniques, reporter gene assays, siRNA, RT-PCR, Northern blotting, EMSA, Western blotting, and HPLC. Other studies in the laboratory pertain to cross-talk between various signaling pathways in neuronal cells, developmental expression of neuronal-specific genes, and the effects of DNA methylation on promoter activity.
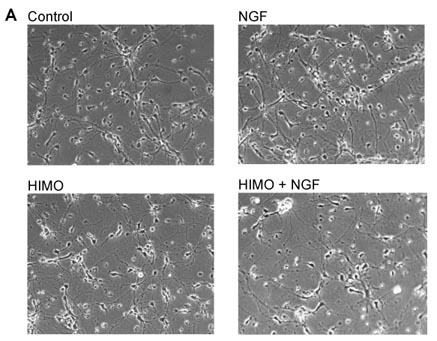
Blocking the PI3K/Akt pathway inhibits NGF-stimulated cholinergic gene expression in primary septal neurons(A) Primary cultures isolated from E18 mouse septum were treated with the Akt inhibitor HIMO (10 µM) for 12 h prior to stimulation with 100 ng/ml NGF. Phase-contrast photographs were taken after 72 hours of treatment. Objective lens 20 x.
(B) E18 primary septal cultures were pre-treated with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (LY) for 1h, or with HIMO for 12 h, and then stimulated with NGF for 72 h. RT/PCR was performed on total RNA with CHT, VAChT and ?-actin primers. The results are representative of three independent experiments.
Recent Publications –
- Madziar B., Shah S., Brock M., Burke R., Lopez-Coviella I., Nickel A.-C., Cakal E.B., Blusztajn J.K., Berse B. (2008) Nerve growth factor regulates the expression of the cholinergic locus and the high-affinity choline transporter via the Akt/PKB signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 107:1284-1293.
- Brock M., Nickel A.C., Madziar B., Blusztajn J.K., Berse B. (2007) Differential regulation of the high affinity choline transporter and the cholinergic locus by cAMP signaling pathways. Brain Res. 1145:1-10.
- Berse B., Szczecinska W., Lopez-Coviella I., Madziar B., Zemelko V., Kaminski R., Kozar K., Lips K.S., Pfeil U., Blusztajn J.K. (2005) Expression of high affinity choline transporter during mouse development in vivo and its upregulation by NGF and BMP-4 in vitro. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 157:132-140.
- Lopez-Coviella I., Follettie M.T., Mellott T.J., Kovacheva V.P., Slack B.E., Diesl V., Berse B., Thies R.S., Blusztajn J.K. (2005) Bone morphogenetic protein 9 induces the transcriptome of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:6984-6989.
- Madziar B., Lopez-Coviella I., Zemelko V., Berse B. (2005) Regulation of cholinergic gene expression by nerve growth factor depends on the phosphatidylinositol-3′-kinase pathway. J. Neurochem 92:767-779.
- Burau K., Stenull I., Huber K., Misawa H., Berse B., Unsicker K., Ernsberger U. (2004) c-ret regulates cholinergic properties in mouse sympathetic neurons: evidence from mutant mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20:353-362.
- Mellott T., Lopez- Coviella I. , Blusztajn J.K., Berse B. (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase negatively modulates ciliary neurotrophic factor-activated choline acetyltransferase gene expression. Eur. J. Biochem. 269:850-858.
- Malik M.A., Greenwood C.E., Blusztajn J.K., Berse B. (2000) Cholinergic differentiation triggered by blocking cell proliferation and treatment with all-trans retinoic acid. Brain Res. 874:178-185.
- Lopez-Coviella I., Berse B. , Krauss R., Thies R.S., Blusztajn J.K. (2000) Bone morphogenetic protein-9 induces and maintains the cholinergic phenotype of neurons in the central nervous system. Science 289:313-316.
- Blusztajn J.K., Berse B. (2000) The cholinergic neuronal phenotype in Alzheimer’s disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 15:45-64.
- Berse B., Lopez-Coviella I., Blusztajn J.K. (1999) Activation of TrkA by nerve growth factor upregulates expression of the cholinergic gene locus but attenuates the response to ciliary neurotrophic factor. Biochem. J. 342:301-308.